Resources Management
A variety of linguistic resources can be managed in SYSTRAN Translate via the Resources menu.
This allows users to implement powerful linguistic resources that are tailored to their translation needs. Users can add Translation Memories and additional dictionaries such as Domain Dictionaries to a Profile in order to improve translations.
Once resources are completed, they can be added to a profile via the Profiles page.
Note
UD and TM cannot be used with pivot profiles.
Permissions
It is possible to share with given users, or with groups the following elements:
User Dictionaries
Translation Memories
For each item, click on the button ‘User Permission’ or ‘Group Permission’ to open the permission assignment pop up:
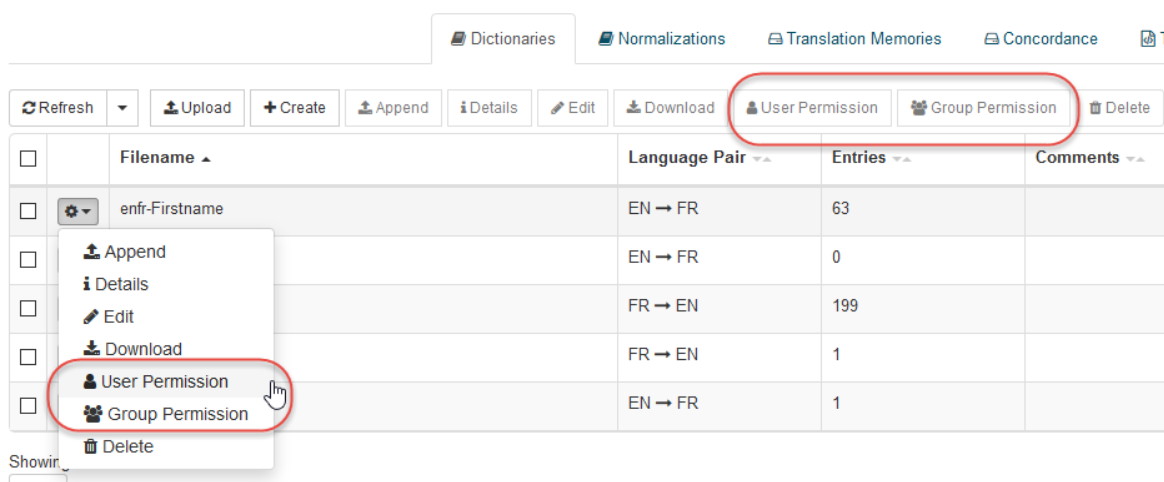
Once you’ve opened the permission pop up, you can assign permissions at the user/group level by selecting the user or group name. Then:
Select the appropriate permission in the toolbar or drop-down menu associated to the user/group (see below for more details)
Click on ‘Save’ for the given user
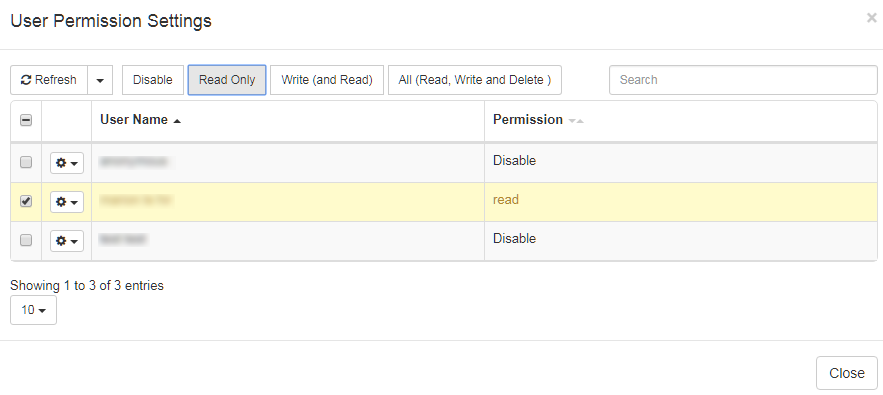
Users or groups can be given the following permissions:
Disable: (by default) the item is not visible Read Only:
the item can be entered in a read only mode from the list (if the user has the permission to access the Resource List, e.g. the Translation Memory menu)
the item can be selected by the user in a profile (if the user has the permission to create profiles)
the item will be included in the Lookup results in the ‘Text Translation’ tools (i.e. elements from the Dictionary or from the Translation memory can appear in the Dictionary Lookup box or in the Translation memory lookup results)
Write’ (and Read): same rights as above, plus
the user can enter and modify the resource
All (Read, Write and Delete): same rights as above, plus
the user can also delete the item, and set the item’s permissions for other users
A permission mechanism will also be implemented on Profiles and active profiles in the upcoming versions.
Dictionaries
User Dictionaries can be assigned to a Profile to improve the quality of your translations. The quality of translation software is directly tied to the level of “understanding” achieved by the system. In order to gain a good level of “understanding,” the system must obtain not only a correct syntactic analysis of the text, but also a correct semantic analysis. This is because some words will have different meanings and syntactic behavior depending on the semantic context in which they are used. User Dictionary entries override the over one million built-in entries contained in SYSTRAN’s main dictionaries during the translation process.
Updating Dictionaries
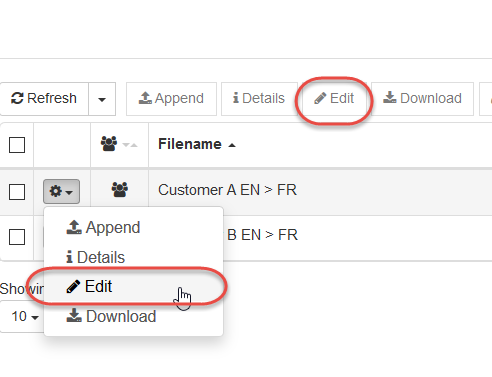
You can take the following actions on dictionaries from the Dictionaries list:
Append → Add entries by uploading file; more details below
Edit → Add and edit entries; more details below
Details → Modify the dictionary’s properties (name, source and target language) and add or edit comments
Download → Download the dictionary
Uploading a Dictionary
To upload entries into the dictionary, select a dictionary, click on the ‘Append’ button then upload a dictionary following the binary format (.dct), Microsoft Excel (.xls) or plain text (.txt).
Note
We recommend to upload UD that does not exceed 200000 segments.
Dictionaries created with a spreadsheet application, such as Microsoft Excel, or a common text editor must be carefully formatted before they can be imported. Below is a detailed description of the format required for dictionaries to be imported.
Microsoft Excel Files
To import dictionaries created with Microsoft Excel, the files must consist of one worksheet for one translation, for example english to french. As with formatted text files, the Microsoft Excel file column headings for the Languages and information columns for the UD must be entered with respecting the 2-letter ISO 639 code language in uppercase.
Formatted Text Files
Formatted text files for import onto SYSTRAN Translate include the document header and the dictionary content. The dictionary’s header is a sequence of lines starting with the “#” character and containing a header field followed by its value. The dictionary’s content is a sequence of lines, with each line representing a dictionary entry whose fields are separated by tab characters. The field types are defined in the header. It is important that each line have the same number of fields, even if they are empty.
Required and Optional Fields for uploading Files onto SYSTRAN Translate:
Header |
Description of Input |
|---|---|
#COVERED DOMAINS= |
Optional header: lists all domains configured in the dictionary
Note: not applicable to NMT
|
#ENCODING= |
Required: defines the encoding of the file. UTF-8 encoding is recommended |
#GENERAL DICTIONARY DOMAINS= |
Optional header: lists the system domains associated with the dictionary
Note: not applicable to NMT
|
#SUMMARY= |
Required: the name of the UD file |
#MULTI/TM/NORM/DNT #<Languages><Informational columns>= |
Required: These two lines are the end of the header section. #MULTI defines that the dictionary is a User Dictionary #TM defines that the dictionary is a Translation Memory #NORM defines that the dictionary is a Normalization Dictionary #DNT is used to separate in a User Dictionary, multilingual entries from DNT entries The second line describes the list of columns in the content section. It is a list of codes separated by tab characters as described in the following table |
Description of the different codes defining the content fields:
Code |
Description |
|---|---|
XX |
Where XX is a 2-letter ISO 639 code in uppercase. This represents a language (Refer to Appendix B. Language Pairs and ISO 639
Codes).The source language is always the first column,with target languages as the following columns
|
XX_NO |
For Normalization Dictionaries only. XX corresponds to the ISO 639 code for the source language. These columns represent
the Normalized columns
|
UPOS |
User Part of Speech. Accepted POS: acronym, adjective, adverb, conjunction, noun, preposition, proper noun, rule, verb (spelled in lowercase).
They correspond to the POS in the interface, except for Expression.
|
HEADWORD_XX |
This column is generated when doing an export. It contains the headword of the corresponding XX field.
During import, this column is ignored
|
PRIORITY |
Priority column
Note: not applicable to NMT
|
DOMAINS |
Domains column. Domains are comma separated
Note: not applicable to NMT
|
FREQUENCY |
Frequency column |
EXAMPLE |
Example column |
Sample Formatted Text File:
The following sample text file is formatted for importing as a User Dictionary onto SYSTRAN Translate. Note that <TAB> indicates the tab character.
#ENCODING=UTF-8
#AUTHOR=SYSTRAN
#EMAIL=[email protected]
#COVERED DOMAINS=Computers/Data Processing,Perso
#GENERAL DICTIONARY DOMAINS=Computers/Data Processing
#PRIORITY=1
#SUMMARY=Demo Computer
#MULTI
#EN<TAB>FR<TAB>NOTE<TAB>DOMAINS<TAB>PRIORITY<TAB>UPOS
white cycle<TAB>cycle d'écriture<TAB>Note<TAB>1<TAB>noun
write enable<TAB>validation écriture<TAB><TAB><TAB>noun
#DNT
#EN<TAB>NOTE<TAB>DOMAINS
Print 2000<TAB>It is a DNT<TAB>Perso
The following sample text file is formatted for importing into SDM as a Translation Memory.
#AUTHOR=SYSTRAN
#EMAIL=[email protected]
#ENCODING=UTF-8
#SUMMARY=Demo
#TM
#EN<TAB>FR<TAB>DE
My name is Smith<TAB>Mon nom est Smith<TAB>Mein Name ist Smith
To use a User Dictionary with a Profile:
Click on Profiles
Select the profiles
Expand the profiles options
In Resources, select the Dictionary wanted
Click Submit
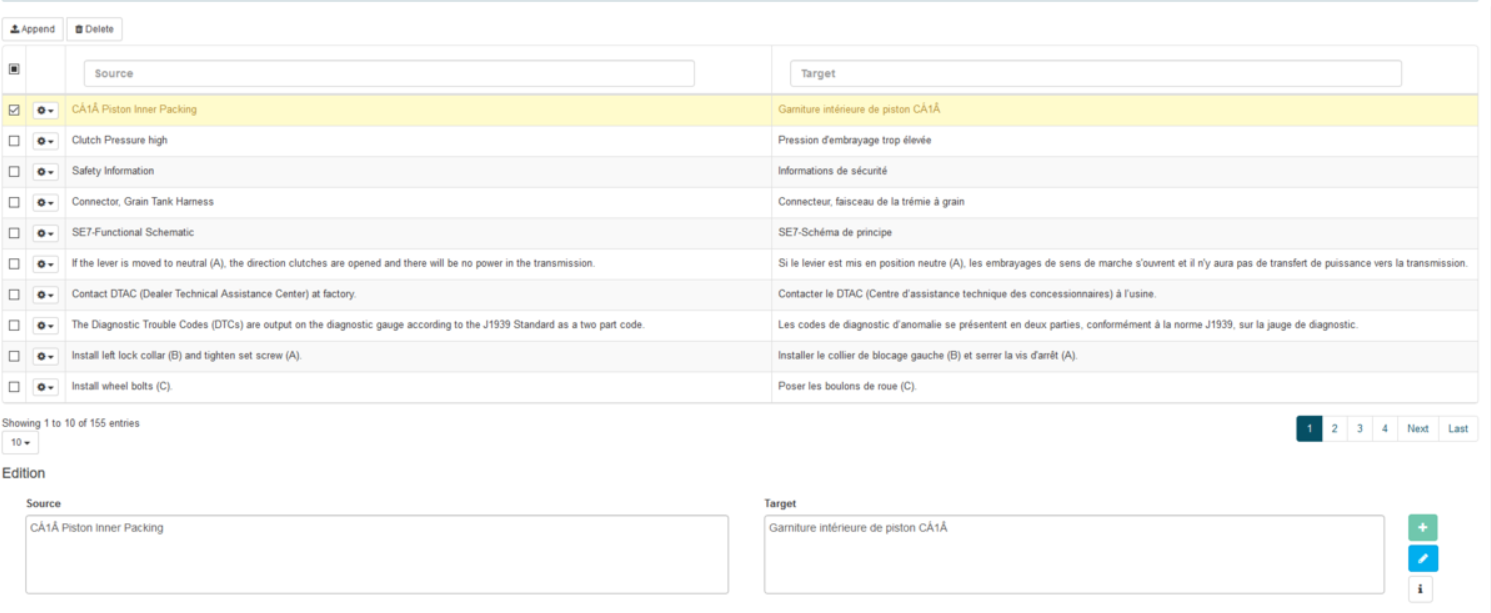
Entries of imported dictionaries can then be modified directly on the server by clicking Edit. Details on how to use this tool are below.
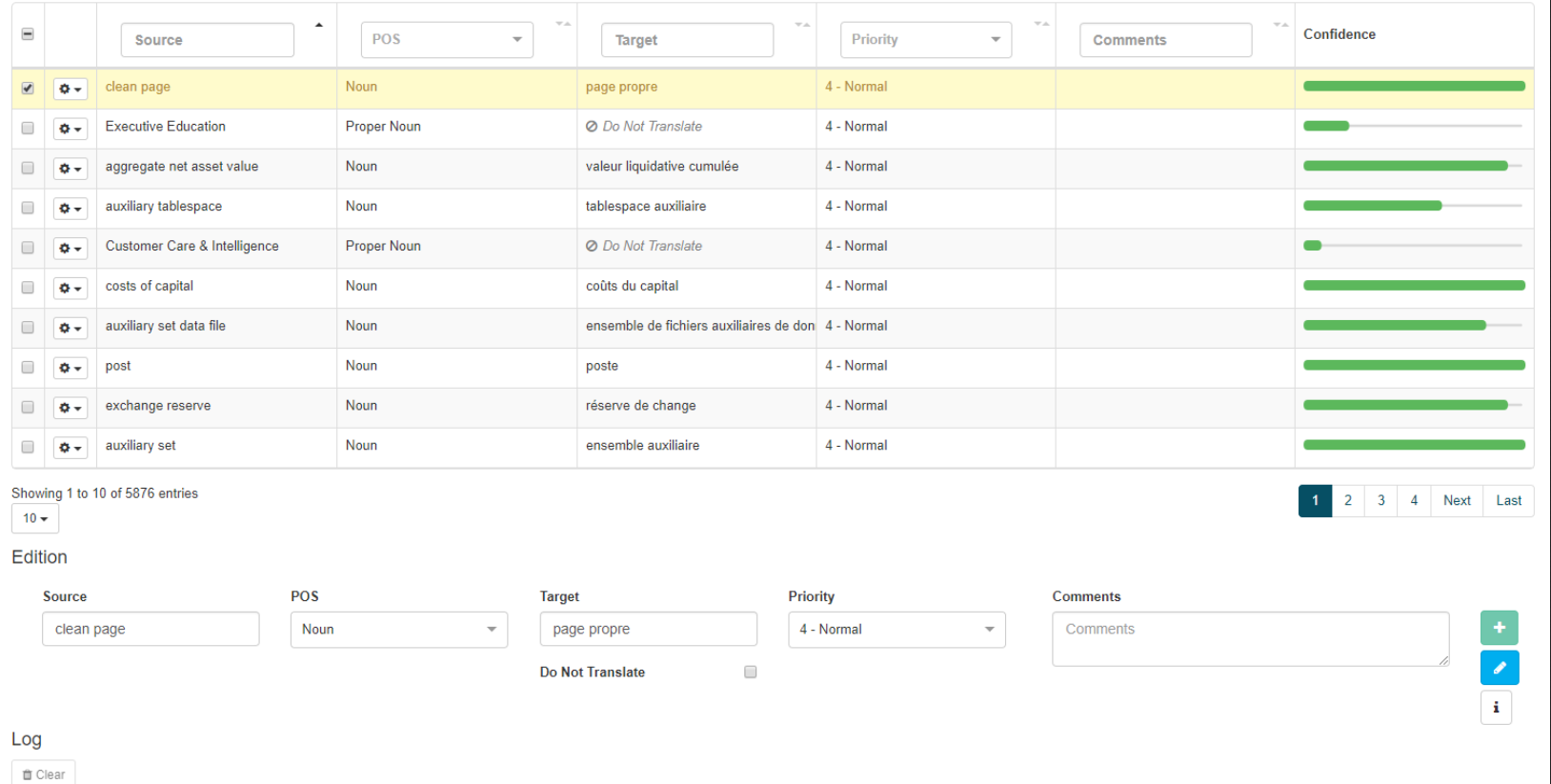
Editing Dictionaries: Editing zone
Below the navigation table is another table (Edition & Log) where existing entries can be modified and new entries appended to the dictionary.
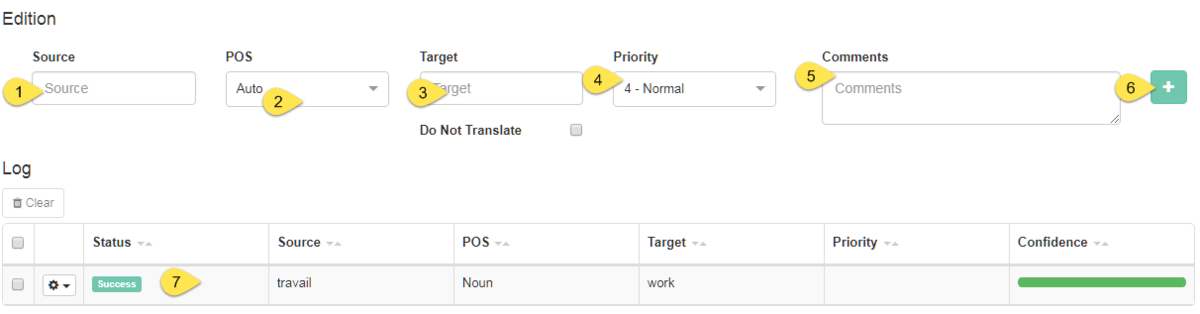
To modify an existing entry, click on the entry’s row in the Dictionary Editor table to highlight it. It will appear in the fields at the bottom of the page. If no entry is highlighted, these fields will be blank and a new entry can be added by filling in the:
Source
POS
Target
Priority
Comments
Click Add (or Edit in the case of the modification of an existing entry)
When an entry is successfully added, its status will be displayed as Coding successful. If this is not the case, contact your Administrator. When adding a new entry, its confidence will also be calculated and displayed
When determining the POS, use the entry’s lemma unless it concerns an expression or rule. By default, assigning a POS is done automatically. If the entry is a proper noun that should not be translated, tick the Do not Translate box. Hover over the information icon on the lower right-hand side of the page to learn how to use keyboard shortcuts.
Downloading Dictionaries
Click Download
Rename the downloaded file with the extension ‘.txt’ to open the file
Dictionary coding
Special characters
hash # can’t be used
some characters need to be need to be protected:
quotes
"and parentheses()should be preceded by a backslash\so that they will be considered as part of the entry, not part of the coding syntax; they will show in the coded entry (without the backslash)backslash
\needs to be entered as\\\\; it will show as\\in the coded entry
note that most dashes (en dash
–, em dash—etc.) will be normalized to hyphen-minus-in the translation input (so if the dictionary entry contains an en dash it won’t match the normalized input)most quotes will be normalized to straight quotes in the translation input, and straight quotes might be normalized to other (locale) quotes in the output
Coding clues
quotes
"can be used to freeze (part of) the entry so that it won’t inflect; the quotes won’t show in the coded entrycoding clues in parentheses for number (sg, pl), gender (m,f,neuter) and other morpho-syntactic information can be used for certain languages
Normalizations
Normalization Dictionaries (NDs) provide a way to regulate text both before and after translation, serving as a means for standardizing terminology and expanding abbreviations and acronyms. NDs can also be used to standardize spellings and to establish common terminology (e.g., instances in which two or more words are used for the same concept).
You can add your Normalization Dictionaries (either for the source language or for the target language) to a profile. In case a Normalization dictionary is indicated for the Source Language, then it will process the source input text before translation. If the Normalization dictionary is for the target language, then it will process the translated text.
To create a new Normalization dictionary, in Resources, click Normalizations then Create to open a dialog box:
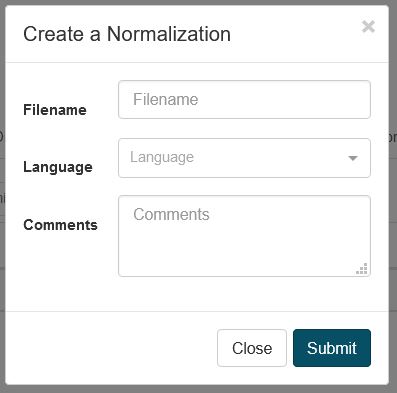
Choose a name for your normalization dictionary and select the language
Click Submit to create the Normalization Dictionary
The same guidelines apply to upload, download and edit a Normalization Dictionary as for a User Dictionary. See the above section on Dictionaries.
When importing a new Normalization dictionary, be sure that the header is the correct format. The following sample text file is formatted for importing a Normalization Dictionary to SYSTRAN Translate. Note that <TAB> indicates the tab character.
#AUTHOR=SYSTRAN
#EMAIL=[email protected]
#SUMMARY=EN NORMALIZATION DICTIONARY
#ENCODING=UTF-8
#COVERED DOMAINS=coll
#GENERAL DICTIONARY DOMAINS=coll
#NORM
#EN EN_NO UPOS DOMAINS NOTE
youre <TAB> you are <TAB> sequence
4ever <TAB> forever <TAB> sequence
Once you’ve created or imported a Normalization dictionary, you can associate it to a profile.
Translation Memories
Translation Memories (TMs) are useful for establishing translation consistency across an array of documented files. TMs are collections of sentence pairs, each of which include a source sentence and its translation, stored in a bilingual or multilingual database. Using a Translation Memory enables words or expressions to be retrieved from previously translated texts during the translation process. Unlike User Dictionary entries - which remain susceptible to linguistic analysis - the sentence translations that exist in TMs are static. When translating a document with a Profile containing TMs, sentences that are present in the memory (exact matches) will override the machine translation. Rather than retranslating that sentence, SYSTRAN simply places the correlating already-translated target sentence into the document.
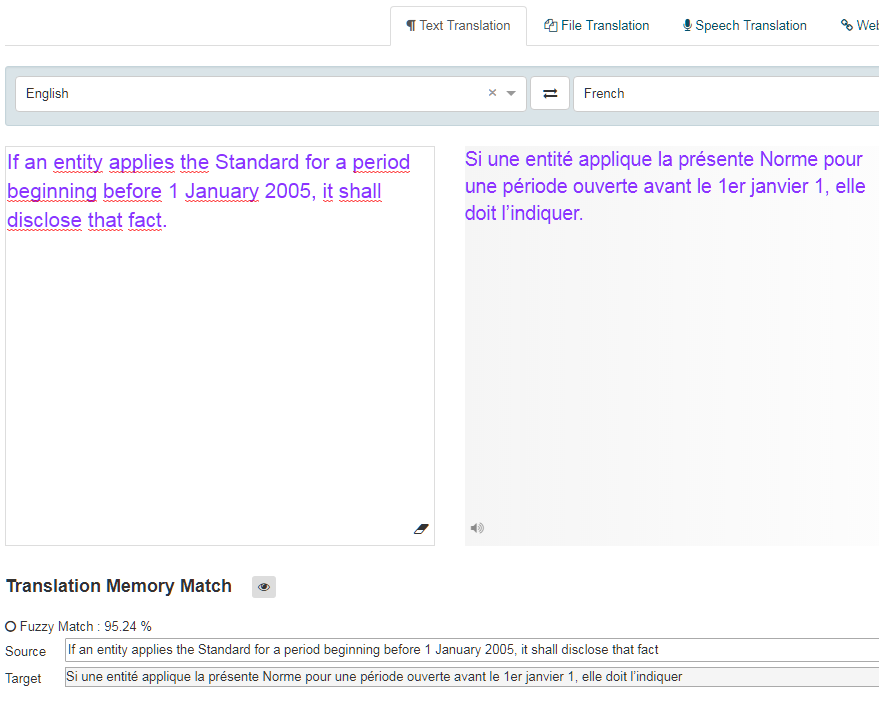
When translating with a translation memory, a segment in the source text that corresponds exactly to a segment in the translation memory database is an exact match with a score of 1.0 (100%) and a segment that corresponds partially is a fuzzy match with a value lower than 1 (<100%). The score compares the input with the translation memory match and calculates the similarities between the two. The higher the score, the closer the match. The database will return any matches higher than the fuzzy match threshold as configured by the administrator (70% by default). These matches will be shown as Fuzzy Match Alternatives in the Text Translation tool and in the Translation Editor when reviewing a file translation.
In the Text Translation box, the fuzzy match will be highlighted in green and the score displayed.
Additionally, Translation Memories may be used as the testing, tuning or training corpus in your translation training projects.
Translation Memory creation
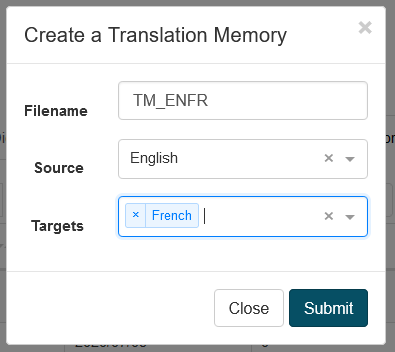
Create Translation Memories
To create a Translation memory, click on the create button, then you will have to file the TM filename, a source language and a targuet language.
Uploading a Translation Memory
Translation Memory eXchange (TMX) files are a specification of XML. SYSTRAN Translate supports TMX versions between 1.2 and 1.4. For more information, see Localization Industry Standards Association’s TMX page.
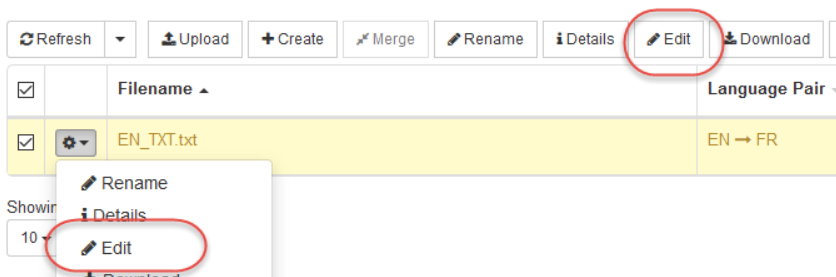
To upload a Translation Memory, click Resources then Translation Memory, then select the Translation Memory wanted and click ‘Edit’. Click on “Append” A dialog box will appear:
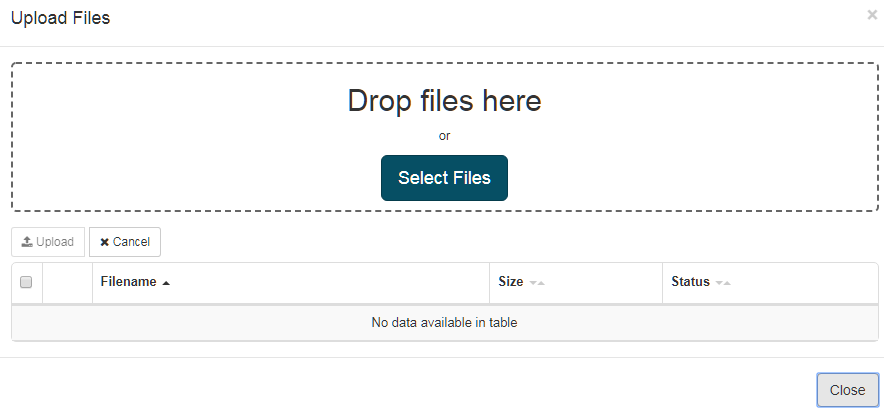
Once uploaded, the entries of the Translation memory will appear on the Translation Memory page.
Note
We recommend to upload TM that does not exceed 200000 segments.
To use a Translation Memory with a Profile:
Click on Profiles
Select the profiles
Expand the profiles options
In Resources, select the Translation Memory wanted
Click Submit
Translation Memories Editor
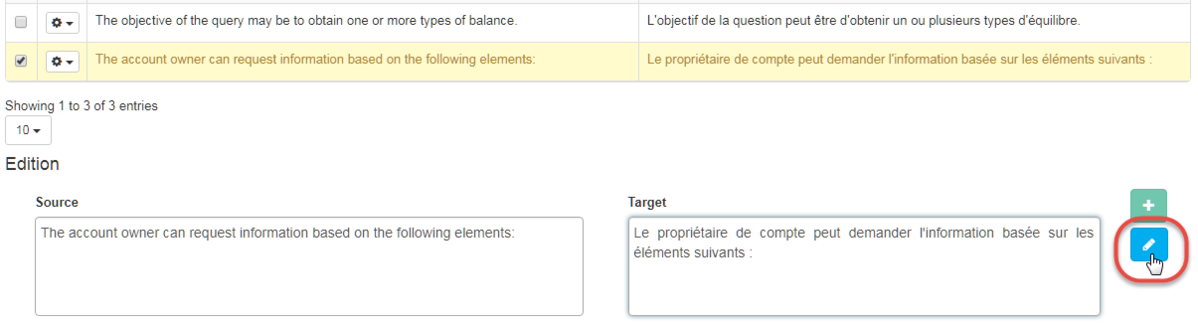
Edit a sentence
Select the entry
Update the required fields (source and/or target)
Click on the button “Edit” or press the Enter key on the keyboard
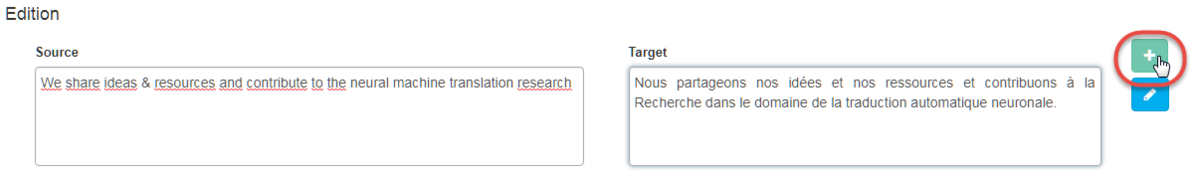
Add a new segment in the Translation Memory
You can directly add an entry via the source and target fields:

Search a sentence
To search for specific sentences, enter the word or sentence you are looking for in the Source or Target segment field:
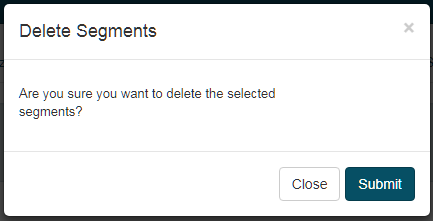
Delete a segment
Select a segment
Click Delete
Click Submit to confirm the deletion